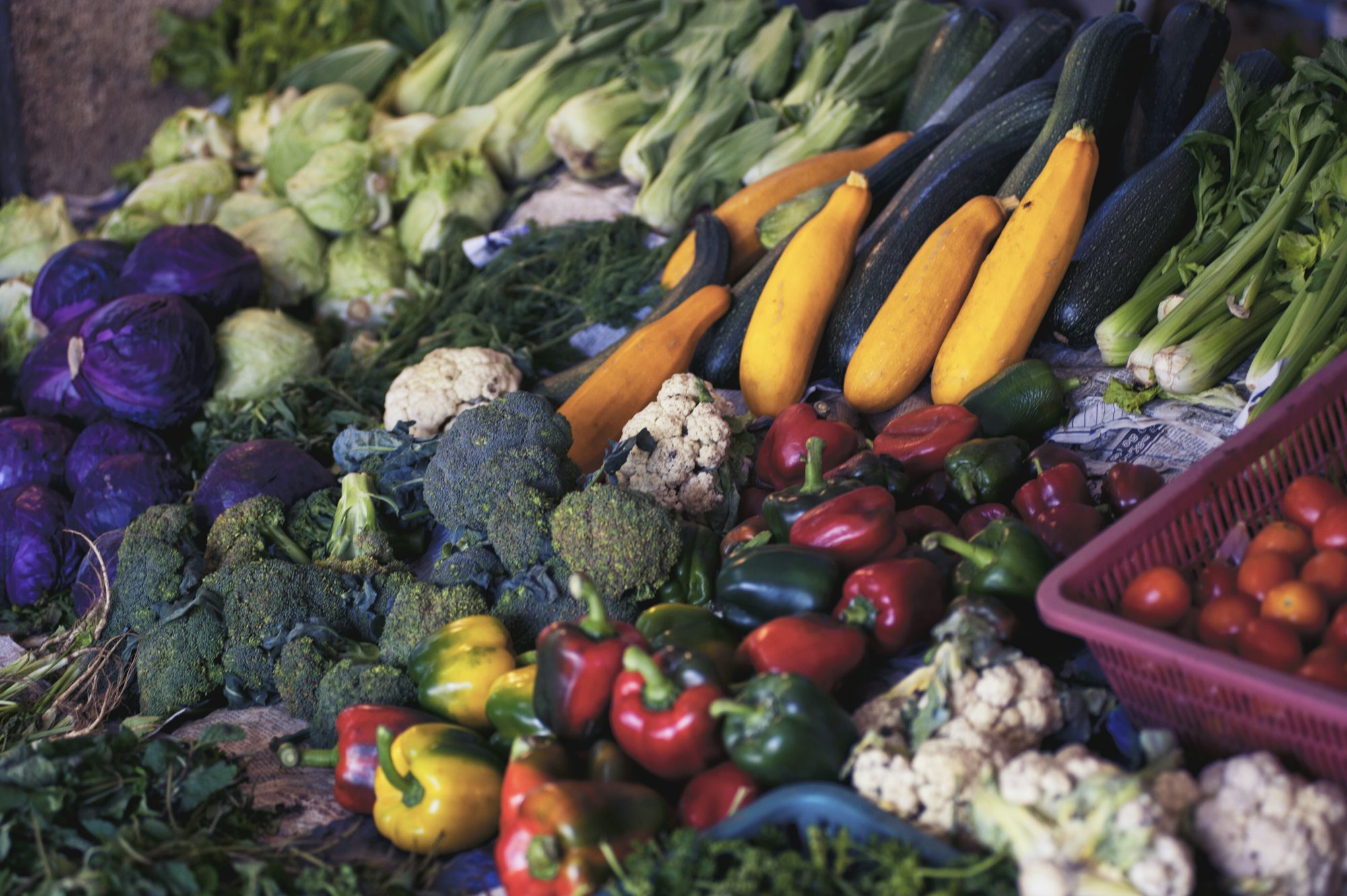
In an era of global food distribution, we often take for granted the variety of ingredients available to us year-round. However, returning to the practice of seasonal eating—choosing foods that are grown and harvested during their natural growing seasons—offers numerous benefits for our health, the environment, and our culinary experiences. This article explores the principles of seasonal eating, its advantages, and practical strategies for embracing this approach in our daily lives.
Seasonal eating is based on the idea that consuming fruits and vegetables at their peak ripeness not only enhances flavor but also maximizes their nutritional value. Foods that are grown in their appropriate seasons tend to be fresher and more nutrient-dense. For instance, vegetables like tomatoes and zucchini are bursting with flavor in the summer, while root vegetables like carrots and potatoes shine in the fall and winter. By aligning our diets with the natural growing cycles of produce, we can enjoy the freshest and most flavorful ingredients available.
One of the primary health benefits of seasonal eating is the increased intake of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Freshly harvested produce is often richer in nutrients than its out-of-season counterparts, which may have been transported long distances or stored for extended periods. Eating a variety of seasonal fruits and vegetables can enhance overall nutrient intake, supporting immune function and promoting optimal health. For example, leafy greens in the spring are an excellent source of vitamins A, C, and K, while fall fruits like apples provide dietary fiber and essential antioxidants.
Additionally, seasonal eating encourages diversity in our diets. By consuming a variety of foods throughout the year, we not only enjoy different flavors and textures but also ensure a broad spectrum of nutrients. This diversity can enhance gut health by supporting a varied microbiome, which plays a crucial role in overall well-being. Incorporating seasonal produce into our meals allows us to explore new ingredients and experiment with different culinary techniques, keeping our meals exciting and satisfying.
Beyond personal health benefits, seasonal eating has a positive environmental impact. When we choose locally grown seasonal produce, we reduce the carbon footprint associated with transportation and storage. This practice supports local farmers and promotes sustainable agriculture, which is essential for the health of our planet. By prioritizing seasonal foods, we contribute to a food system that values sustainability and ecological balance.
To successfully incorporate seasonal eating into your lifestyle, consider the following practical tips:
1. Know Your Seasons: Familiarize yourself with the growing seasons of fruits and vegetables in your region. Seasonal calendars can help you identify what’s in season and when. This knowledge allows you to plan meals around available ingredients.
2. Visit Local Farmers’ Markets: Farmers’ markets are excellent sources of fresh, seasonal produce. Engaging with local farmers can provide insights into what’s currently being harvested and inspire you to try new foods.
3. Join a Community Supported Agriculture (CSA) Program: CSAs allow you to buy a share of a local farm’s produce, providing you with a weekly supply of fresh, seasonal fruits and vegetables. This not only supports local agriculture but also encourages you to explore new ingredients and recipes.
4. Plan Seasonal Meals: When planning your weekly meals, prioritize seasonal ingredients. Create a meal plan that highlights fresh produce, allowing you to take advantage of what’s available. This approach can help you reduce food waste and save money.
5. Experiment with Preserving: If you find yourself with an abundance of seasonal produce, consider preserving it through canning, freezing, or drying. This way, you can enjoy the flavors of the season even when certain foods are no longer in season.
6. Be Flexible: While it’s helpful to plan meals around seasonal ingredients, it’s also important to remain flexible. Be open to trying new foods and adapting recipes based on what’s available. This flexibility can lead to delightful culinary discoveries.
7. Share Recipes and Ideas: Engage with friends and family about seasonal eating. Share recipes, cooking tips, and ideas for utilizing seasonal ingredients. This can create a sense of community and inspire others to embrace seasonal eating as well.
Incorporating seasonal eating into your life can lead to a richer and more rewarding culinary experience. As you become more attuned to the rhythms of nature, you may find that your meals are not only healthier but also more enjoyable. The flavors of seasonal ingredients are often unmatched, leading to dishes that are vibrant and satisfying.
As we embrace the practice of seasonal eating, it’s important to recognize that it doesn’t have to be a strict guideline. The goal is to cultivate a more mindful and conscious approach to food, appreciating the natural cycles of our environment. Whether you’re enjoying a summer tomato salad or a hearty winter stew, each meal offers an opportunity to connect with the seasons and the land from which our food comes.
In conclusion, seasonal eating is a practice that promotes health, sustainability, and culinary joy. By choosing to eat foods at their peak, we can enhance our well-being while supporting local agriculture and reducing our environmental impact. The journey toward seasonal eating invites us to explore new flavors, foster a deeper connection to our food, and cultivate a more sustainable food system. As we embrace the seasons, we not only nourish ourselves but also contribute to the health of our planet and our communities.